
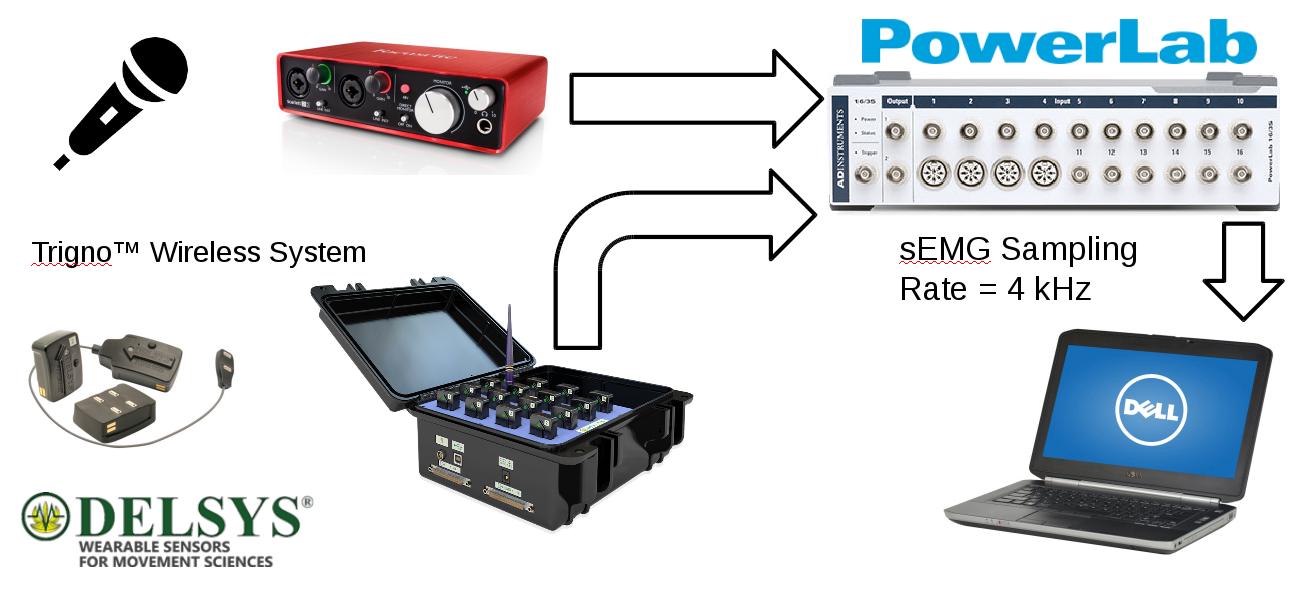
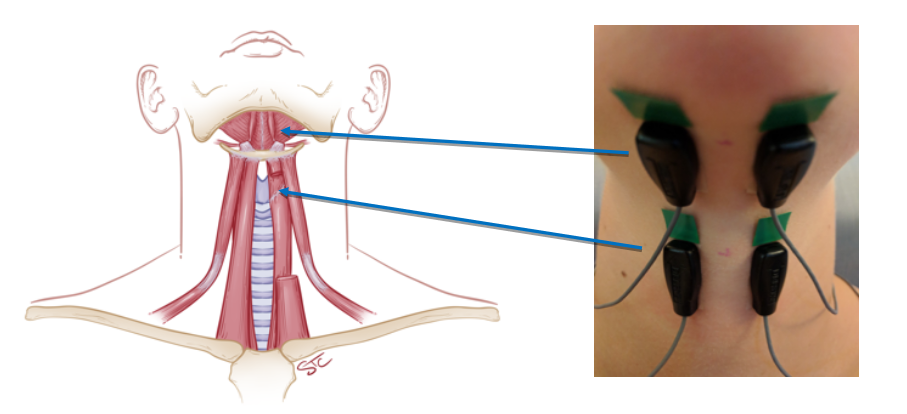
Classification of sEMG signals for vocal fatigue
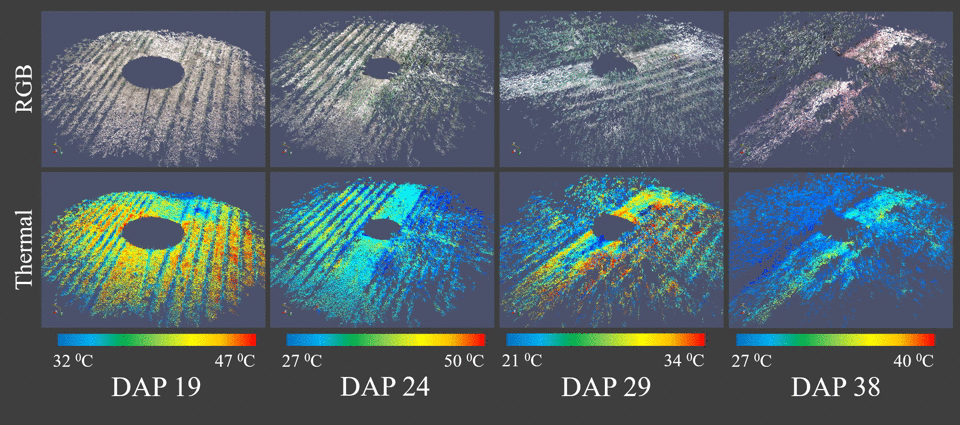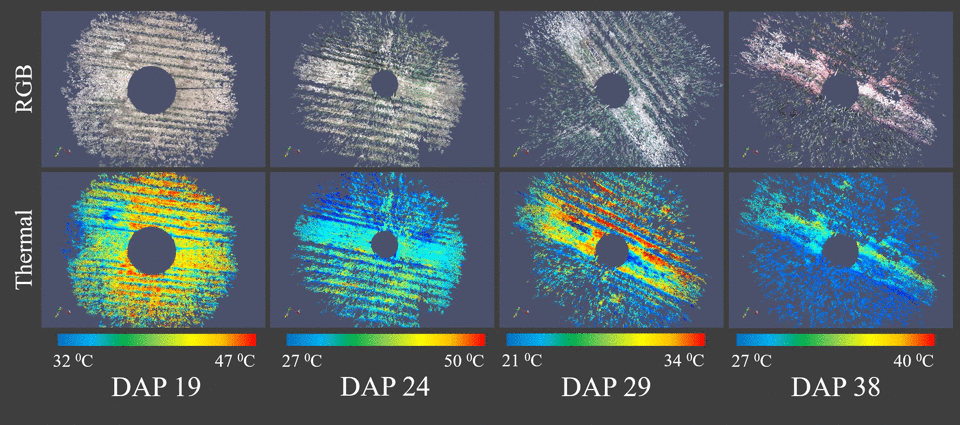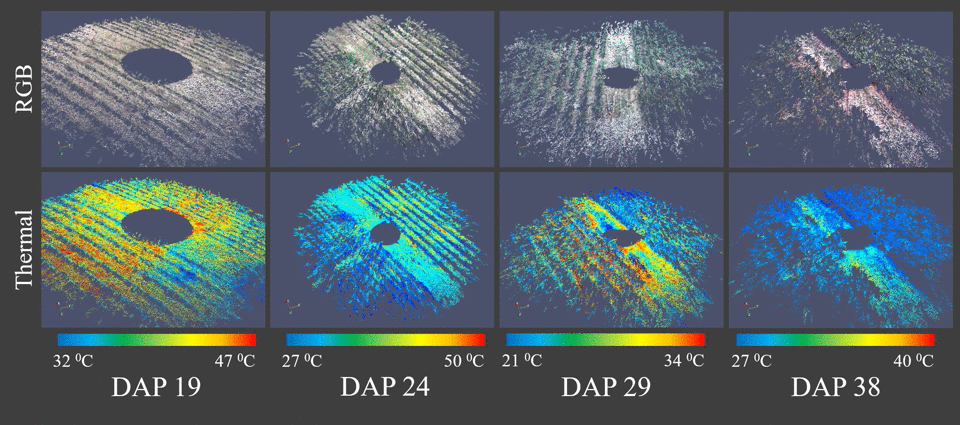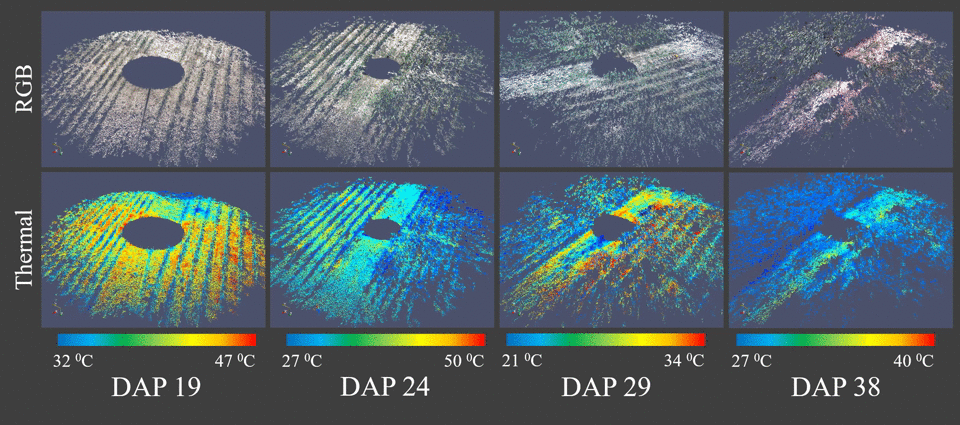
Crop Residue Cover Estimation from High-Resolution RGB Images using Machine Learning Techniques
QAGT-MLP: An Attention-Based Graph Transformer for Small and Large-Scale Quantum Error Mitigation
Foreground object detection is an essential task in many image processing and image understanding algorithms, in particular for video surveillance. Background subtraction is a commonly used approach to segment out foreground objects from their background. In real world applications, temporal and spatial changes in pixel values such as due to shadows, gradual/sudden changes in illumination, etc. make modeling backgrounds a quite difficult task.
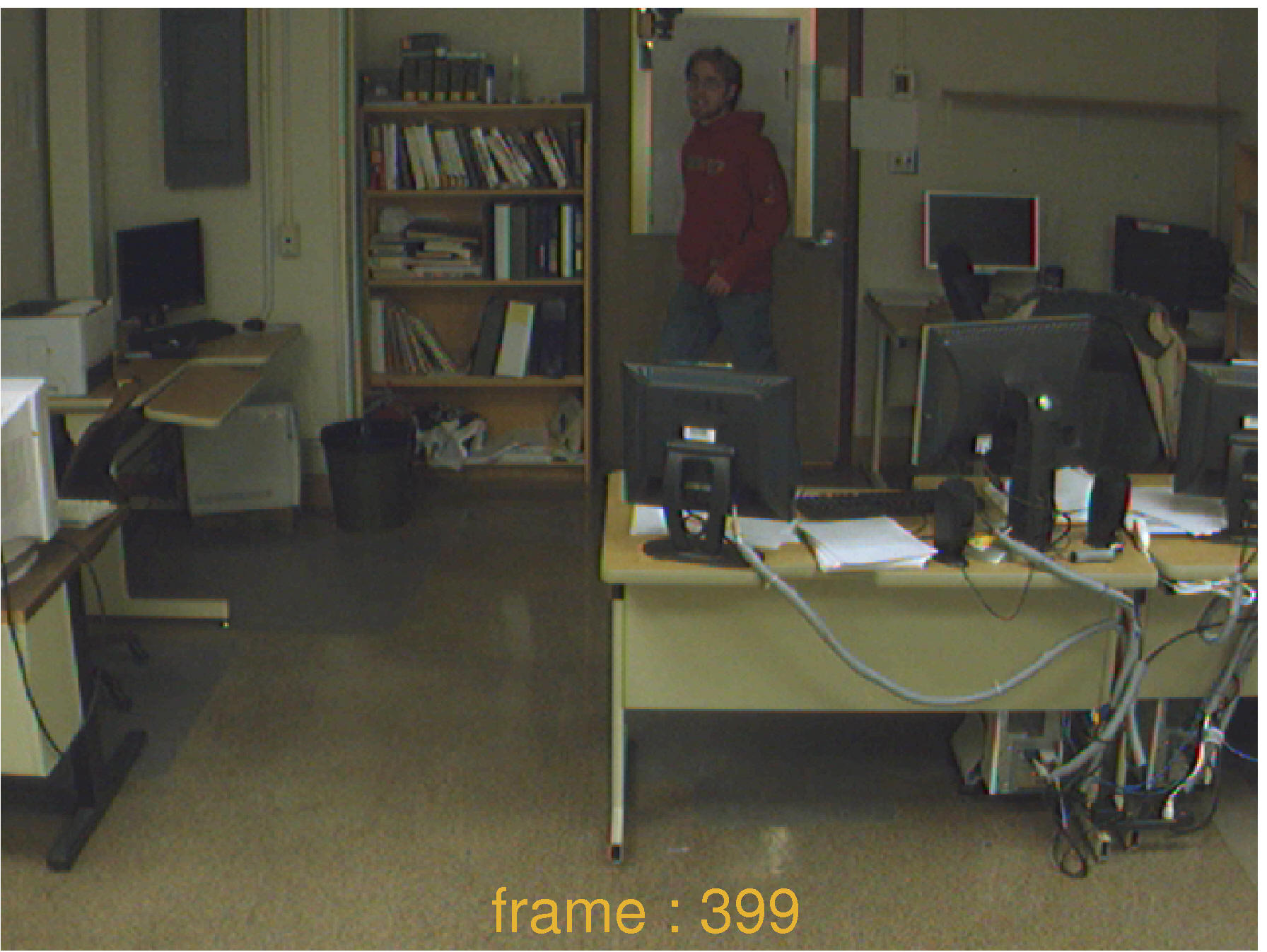


In our work, we propose an adaptive learning algorithm of multiple subspaces (ALPCA) to handle sudden/gradual illumination variations for background subtraction.
Human motion capture has numerous application in human-robot interaction, law enforcement, surveillance, entertainment, sports, medicine, etc. Various methods have been developed to date and they can be categorized into: marker-based or markerless; articulated model-based or appearance-based; single view or multiple view; and so on. Marker-based methods are the simplest ones and therefore are also the methods with most success so far. However, it is obviously not always possible to add markers to the human subjects, and markerless approaches are without a doubt the most general and desirable methods.
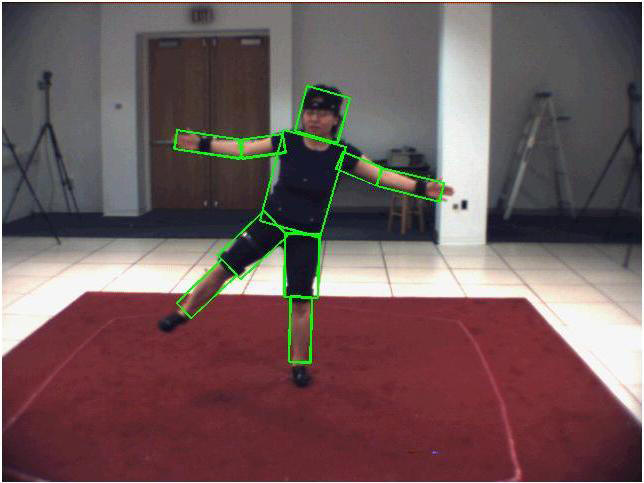
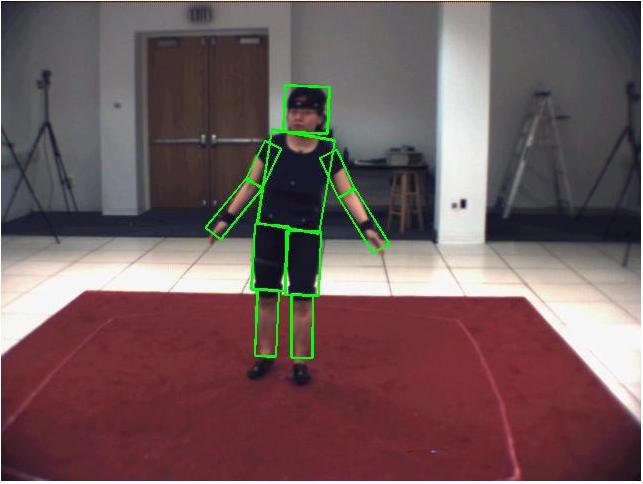

In our work, we explore markerless method for human motion capture. We propose a Bayesian estimation based method which falls into single view and articulated model-based category. The estimator, derived from Particle Filters, was expanded to a hierarchical model by introducing a new coarse-to-fine framework to deal with the computational complexity inherent to Particle Filters.
Any control system using visual-sensory feedback loops falls into one of four categories. These categories are derived from choices made regarding two criteria: the coordinate space of the error function, and the hierarchical structure of the control system. These choices will determine whether the system is a position-based or an image-based system, as well as if it is a dynamic look-and-move or a direct visual servo.
In our work, we present an image-based, dynamic look and move visual servoing system. The difference between our approach and other popular ones is in the use of quaternion representation, which eliminates the potential singularities introduced by a rotational matrix representation.